Assessment of groundwater suitability using remote sensing and GIS: a case study of Western Rajasthan, India

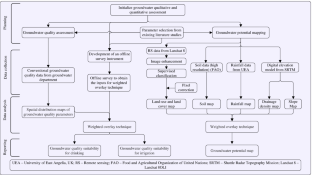
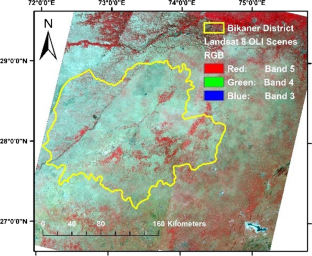
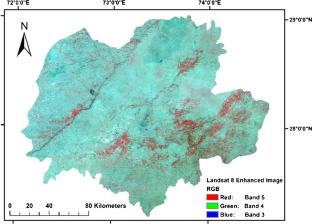
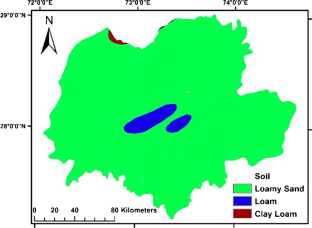
The overexploitation of natural freshwater resources has been observed in recent years, leading not only to a depletion of the groundwater table but also to degradation in the groundwater quality. This situation is more serious in the arid to hyper-arid regions. To ensure sustainable management of groundwater, it is essential to investigate the improved mechanism for the integrated use of groundwater for rural and urban communities. With the fast advancement in the area of remote sensing (RS) and geographical information systems (GIS), it has now become possible to make an estimate of the Earth’s resources with high accuracy both spatially and temporally. The current study attempts to describe potential zones of the availability of groundwater and its quality status based upon the water quality parameters’ spatial distribution by applying a GIS approach integrated with remote sensing technique. All suitable data has been created by developing thematic layers of critical parameters such as rainfall, land use, soil map, slope, land cover, drainage density, and Digital Elevation Model (DEM) using Landsat 8 imagery from Earth Explorer, United State Geological Survey (USGS), and other conventional datasets. Groundwater maps have been prepared using GIS by keeping in view the relative importance of thematic layers. The outcomes of the study will allow users to identify, visualize, understand, assess, and analyze the suitability of groundwater quality as well as quantity.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save
Springer+ Basic
€32.70 /Month
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Buy Now
Price includes VAT (France)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve


Similar content being viewed by others
Delineation of suitable sites for water conservation structures and groundwater potential zones using integration of remote sensing and GIS: a case study of Central India
Article 04 April 2024

Identification of Groundwater Recharge Potential Zones and Groundwater Quality Mapping Using Remote Sensing and GIS
Chapter © 2022
Mapping of Groundwater Potential Zone Based on Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques: A Case Study of Kalmykia, Russia
Article 01 January 2019
Data availability
All necessary data supporting the findings are available in the manuscript. If any additional data would be required by the readers, the same would be shared by the authors electronically whenever it is required.
References
- ArcGIS 10.2. (2019) ArcGIS Enterprise | Enterprise GIS Mapping Platform [Online] Available at http://www.esri.com/software/arcgis/arcgisserver. Accessed 16 Jan 2019
- Barsi JA, Lee K, Kvaran G, Markham BL, Pedelty JA (2014) The spectral response of the Landsat-8 operational land imager. Remote Sensing 6(10):10232–10251. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs61010232ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Bhakar, P. and Singh, A.P., 2018. Groundwater quality assessment in a hyper-arid region of Rajasthan, India. Natural Resources Research, pp.1–18. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-018-9405-
- Bhat SA, Meraj G, Pandit AK (2016) Assessing the influence of stream flow and precipitation regimes on water quality of the major inflow stream of Wular Lake in Kashmir Himalaya. Arab J Geosci 9(50):1–15 Google Scholar
- Bhat, S. A., Meraj, G., Yaseen, S., & Pandit, A. K., 2014. Statistical assessment of water quality parameters for pollution source identification in Sukhnag stream: an inflow stream of lake Wular (Ramsar Site), Kashmir Himalaya. Journal of Ecosystems. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/898054
- Catroll D (1962) Rainwater as a chemical agent of geological process — a view. USGS Water Supply 1533:18–20 Google Scholar
- Chaudhary BS, Kumar S (2018) Identification of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing and GIS of KJ Watershed, India. J Geol Soc India 91(6):717–721 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Corner BR, Narayanan RM, Reichenbach SE (2003) Noise estimation in remote sensing imagery using data masking. Int J Remote Sens 24(4):689–702 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Dar IA, Sankar K, Dar MA (2010) Remote sensing technology and geographic information system modeling: an integrated approach towards the mapping of groundwater potential zones in Hardrock terrain, Mamundiyar basin. J Hydrol 394(3–4):285–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.08.022ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Davis S.N. and DeWeist R.J.M.1966, Hydrogeology, Wiley, New York
- Eaton FM (1950) Significance of carbonate in irrigation water. J Soil Sci 69(2):123–134 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- FAO (2019). Digital soil map of the world. Food and Agricultural Organization of United Nations. Available at: http://www.fao.org/geonetwork/srv/en/metadata.show?id=14116 (Accessed 15 Jan. 2019).
- Freeze R A & Cherry J A 1979, Groundwater — chapter 9, pp. 430–432, Prentice Hall Inc. Englewood, Cliffs. New Jersey.
- Ganapuram S, Kumar GV, Krishna IM, Kahya E, Demirel MC (2009) Mapping of groundwater potential zones in the Musi basin using remote sensing data and GIS. Adv Eng Softw 40(7):506–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2008.10.001ArticleGoogle Scholar
- He S, Li P, Wu J, Elumalai V, Adimalla N (2020) Groundwater quality under land use/land cover changes: a temporal study from 2005 to 2015 in Xi’an, northwest China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J 26(10):2771–2797 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Hexagonal Geospatial 2015, ERDAS IMAGINE 15.00.00 Release Notes, Available at: https://community.hexagongeospatial.com/t5/IMAGINE-Release-Information/ERDAS-IMAGINE-15-00-00-Release-Notes/ta-p/3218 (Accessed 16 Jan. 2019).
- Hussein AA, Govindu V, Nigusse AGM (2017) Evaluation of groundwater potential using geospatial techniques. Appl Water Sci 7(5):2447–2461 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- IDEI, 2018, Water India facts, International Development Enterprises, India, available on: http://www.ide-india.org/content/water-india-facts (accessed on 12/01/2019).
- Iqbal J, Gorai AK, Katpatal YB, Pathak G (2015) Development of GIS-based fuzzy pattern recognition model (modified DRASTIC model) for groundwater vulnerability to pollution assessment. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12(10):3161–3174 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Jenifer MA, Jha MK (2017) Comparison of analytic hierarchy process, catastrophe and Entropy techniques for evaluating groundwater prospect of hard-rock aquifer systems. J Hydrol 548:605–624 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Jensen JR (1996) Introductory to digital image processing; a remote sensing perspective, 2nd edition. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey
- Jha MK, Chowdhury A, Chowdary VM, Peiffer S (2007) Groundwater management and development by integrated remote sensing and geographic information systems: prospects and constraints. Water Resour Manage 21(2):427–467 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Kamra SK, Lal K, Singh OP, Boonstra J (2002) Effect of pumping on temporal changes in groundwater quality. Agric Water Manag 56(2):169–178 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Karnath K R 1987, Groundwater assessment, development and management, Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi, pp. 720.
- Kaur R, Singh RV (2011) Assessment for different groundwater quality parameters for irrigation purposes in Bikaner City Rajasthan. J Appl Sci Environ Sanit 6(3):385–392 Google Scholar
- Khalil MH, Ahmed KS, Elnahry AEH, Hasan AN (2014) Integrated geophysical, remote sensing and GIS studies for groundwater assessment, Abu Zenima Area, West Sinai, Egypt, Int J Geosci, 5, 882-907.
- Kim HK, Kim KH, Yun ST, Oh J, Kim HR, Park SH, . & Kim TS (2019) Probabilistic assessment of potential leachate leakage from livestock mortality burial pits: a supervised classification approach using a Gaussian mixture model (GMM) fitted to a groundwater quality monitoring dataset. Process Saf Environ Prot, 129, 326-338.
- Kumar RP, Ranjan RK, Ramanathan AL, Singh SK, Srivastava PK (2015) Geochemical modeling to evaluate the mangrove forest water. Arab J Geosci 8(7):4687–4702 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Lillesand T, Kiefer RW, Chipman J (2014) Remote sensing and image interpretation. (4th ed.), John Wiley & Sons, New York: Wiley.
- Machiwal D, Singh PK (2015) Comparing GIS-based multi-criteria decision-making and Boolean logic modelling approaches for delineating groundwater recharge zones. Arab J Geosci 8(12):10675–10691 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Magesh NS, Chandrasekar N, Soundranayagam JP (2012) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Theni district, Tamil Nadu, using remote sensing, GIS and MIF techniques. Geosci Front 3(2):189–196 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Manap MA, Nampak H, Pradhan B, Lee S, Sulaiman WNA, Ramli MF (2014) Application of probabilistic-based frequency ratio model in groundwater potential mapping using remote sensing data and GIS. Arab J Geosci 7(2):711–724 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Meraj G, Romshoo SA, Ayoub S, Altaf S (2018) Geoinformatics based approach for estimating the sediment yield of the mountainous watersheds in Kashmir Himalaya India. Geocarto International 33(10):1114–1138 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Mogaji KA, San Lim H (2017) Application of a GIS-/remote sensing-based approach for predicting groundwater potential zones using a multi-criteria data mining methodology. Environ Monit Assess 189(7):1–26 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Naghibi S, Vafakhah M, Hashemi H, Pradhan B, Alavi S (2018) Groundwater augmentation through the site selection of floodwater spreading using a data mining approach (case study: Mashhad Plain, Iran). Water 10(10):1405 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Oikonomidis D, Dimogianni S, Kazakis N, Voudouris K (2015) A GIS/remote sensing-based methodology for groundwater potentiality assessment in Tirnavos area, Greece. J Hydrol 525:197–208 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Pal S, Kundu S, Mahato S (2020) Groundwater potential zones for sustainable management plans in a river basin of India and Bangladesh. J Clean Prod 257:120311 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Pall IA, Meraj G, Romshoo SA (2019) Applying integrated remote sensing and field-based approach to map glacial landform features of the Machoi Glacier valley,NW Himalaya. SN Applied Sciences 1(5):1–11 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Patra S, Mishra P, Mahapatra SC (2018) Delineation of groundwater potential zone for sustainable development: a case study from Ganga Alluvial Plain covering Hooghly district of India using remote sensing, geographic information system and analytic hierarchy process. J Clean Prod 172:2485–2502 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Prasad RK, Mondal NC, Banerjee P, Nandakumar MV, Singh VS (2008) Deciphering potential groundwater zone in hard rock through the application of GIS. Environ Geol 55(3):467–475 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Prasanth SS, Magesh NS, Jitheshlal KV, Chandrasekar N, Gangadhar K (2012) Evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in the coastal stretch of Alappuzha District, Kerala, India. Appl Water Sci 2(3):165–175 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Praveena SM, Lin CY, Aris AZ, Abdullah MH (2010) Groundwater assessment at Manukan Island, Sabah: multidisplinary approaches. Nat Resour Res 19(4):279–291 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Rabinove CL, Lonngfor RH & Brookhart JW 1958, Saline water resources of North Dakota, US Geol. Sur. Water Supply paper, vol.1428, pp.72. US Govt. Print. Off.
- Rao NS (2006) Seasonal variation of groundwater in parts of Guntur District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geol 49(3):413–429 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Richards LA (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline alkali soils, US Department of Agriculture, Handbook, vol. 60, pp. 160. Washington
- Samake M, Tang Z, Hlaing W, M’Bue N, Kasereka K (2010) Assessment of groundwater pollution potential of the Datong Basin, Northern China. J Sustain Dev 3(2):140–152 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Saraf AK, Chowdhary SP (1998) Integrate remote sensing and GIS for groundwater exploration and identification of artificial recharge site. Int J Remote Sens 19(10):1825–1841 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Senanayake IP, Dissanayake DMDOK, Mayadunna BB, Weerasekera WL (2016) An approach to delineate groundwater recharge potential sites in Ambalantota, Sri Lanka using GIS techniques. Geosci Front 7(1):115–124 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Shakerkhatibi M, Mosaferi M, Pourakbar M, Ahmadnejad M, Safavi N, Banitorab F (2019) Comprehensive investigation of groundwater quality in the north-west of Iran: physicochemical and heavy metal analysis. Groundw Sustain Dev 8:156–168 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Shalaby A, Tateishi R (2007) Remote sensing and GIS for mapping and monitoring land cover and land-use changes in the Northwestern coastal zone of Egypt. Appl Geogr 27(1):28–41 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Singh CK, Mukherjee S (2015) Aqueous geochemistry of fluoride enriched groundwater in arid part of Western India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(4):2668–2678 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Singh AP, Chakrabarti S, Kumar S, Singh A (2017) Assessment of air quality in Haora River basin using fuzzy multiple-attribute decision making techniques. Environ Monit Assess 189:373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6075-3ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Singh AP, Khakolia A, Tavanshetti S, Yadav J (2019a) Groundwater quality assessment using GIS and fuzzy logic—a case study of Jhunjhunu district. Pollut Res 38(3):655–662 Google Scholar
- Singh AP, Dhadse K, Ahalwat J (2019b) Managing water quality of a river using an integrated geographically weighted regression technique with fuzzy decision-making model. Environ Monit Assess 191(6):378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7487-zArticleGoogle Scholar
- Singh AP, Bhakar P (2020) Development of groundwater sustainability index: a case study of western arid region of Rajasthan, India. Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00654-9
- Singh P, Anand A, Srivastava PK, Singh A, Pandey PC (2021) Delineation of groundwater potential zone and site suitability of rainwater harvesting structures using remote sensing and in situ geophysical measurements. Advances in Remote Sensing for Natural Resource Monitoring, 170–188.
- Srinivas R, Bhakar P, Singh AP (2015) Groundwater quality assessment in some selected area of Rajasthan, India using fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making tool. Aquatic Procedia 4:1023–1030 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Srinivas R, Singh AP, Gupta AA, Kumar P (2018) Holistic approach for quantification and identification of pollutant sources of a river basin by analyzing the open drains using an advanced multivariate clustering. Environ Monit Assess 190(12):720 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- UEA (2019) High-resolution gridded datasets (and derived products), Climatic Research Unit, University of East Anglia, UK. Available on https://crudata.uea.ac.uk/cru/data/hrg/. Accessed 5 Jan 2020
- Verma P, Singh P, Srivastava SK (2020) Development of spatial decision-making for groundwater recharge suitability assessment by considering geoinformatics and field data. Arab J Geosci 13(8):1–18 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- WHO 2008, Guideline for drinking water quality — second addendum, Vol. 1, Recommendations, pp. 1–4, World Health Organization, Geneva.
- Wilcox LV (1955) Classification and use of irrigation waters, US Department of Agriculture, Circular 969, Washington, DC, USA.
Acknowledgements
Special thanks are due to the Advanced Research Laboratory in Environmental Engineering and Fecal Sludge Management (ARLEE-FSM) of the Civil Engineering Department, BITS Pilani at which this research was carried out. The references cited in this manuscript are also fully acknowledged by the authors and are thankful to the contributors who participated in the questionnaire survey to perform this study. Authors express their sincere thanks to the anonymous reviewers and editors for their valuable suggestions and efforts.
Funding
The authors are also thankful to Aditya Birla Finance Ltd., Veraval, Gujrat for the financial funding to support the Advanced Research Laboratory in Environmental Engineering and Fecal Sludge Management (ARLEE-FSM) of the Civil Engineering Department, BITS Pilani.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Civil Engineering Department, Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani, 333031, India Prashant Bhakar, Ajit Pratap Singh & Ravi Kant Mittal
- Civil Engineering Department, Engineering College Bikaner, Rajasthan, Bikaner, 334001, India Prashant Bhakar
- Prashant Bhakar

















